目次
ちょっと興味があるので、訳してみました。(Wikiのページはこちら) 更新されているようなので、もとの文章も残しておきます。(ページ下部の続きはこちら部分以降) 全部訳そうと思ったのですが、終わらなかったので、まずは前半部分です。まだ、訳しただけで理解できてない。。。 (英語力のなさをさらけ出してしまうのですが、これも修行です。。。おかしいところはツッコミを。)
What is SolrCloud?
Solrクラウドはクラウドでの検索サービスとしてのSolrを管理、運用するための既存のSolrを拡張するものです。
用語集
- Cluster:クラスタは1単位として管理されるSolrノードの集合です。クラスタ全体で単一のschema、solrconfigをもたないといけません。
- Node:ひとつのJVMインスタンスで起動しているSolrのこと
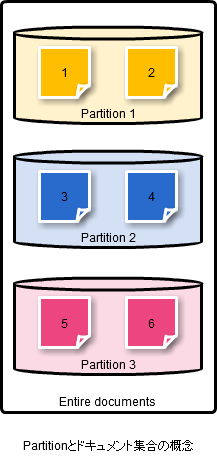
- Partition:パーティションはドキュメント集合全体のサブセット(部分集合)のことです。パーティションは部分集合のドキュメントが単一のインデックスに含まれるような形で作られます。
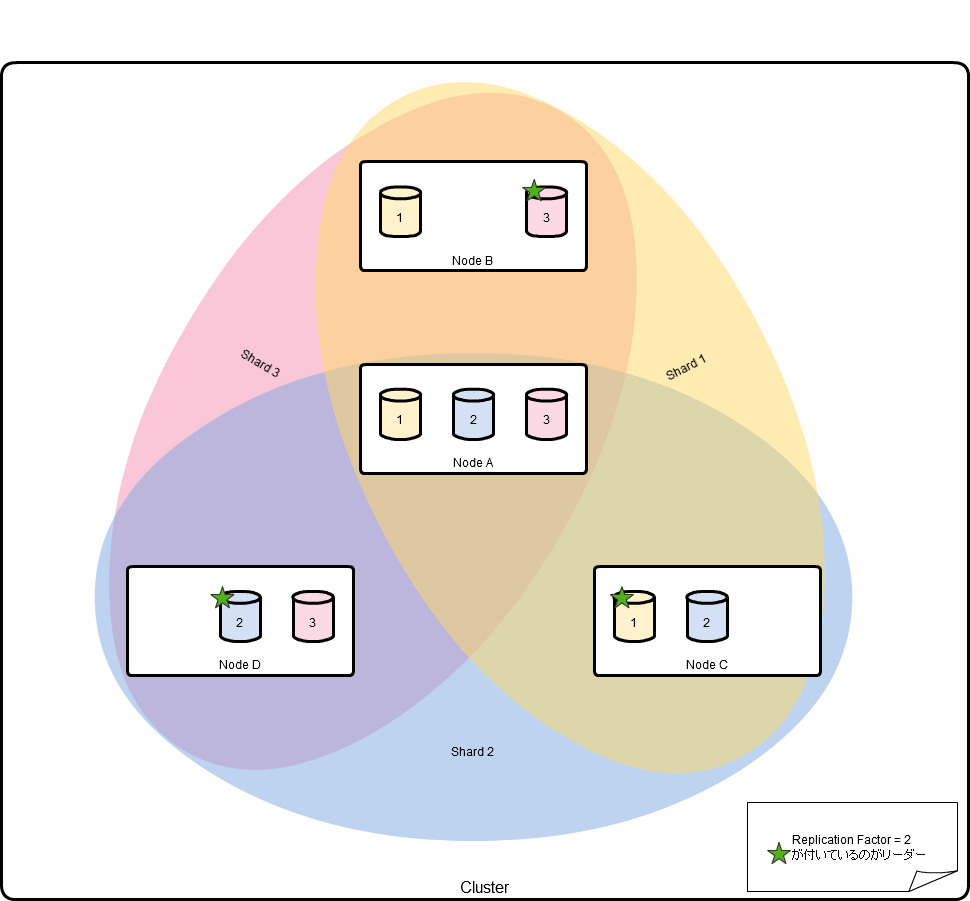
- Shard:パーティションはn(=replication factor)個のノードに保存される必要があります。このn個のノードすべてでひとつのshardです。1つのノードはいくつかのshardの一部にで有る場合があります。
- Leader:各Shardは1つのリーダとなるノードを持っています。パーティションに登録されたドキュメントリーダーからコピーされます
- Replication Factor:クラスタによって保持されるレプリカの最小限の数
- Transaction Log:各ノードによって保持される書き込み処理の追記ログ
- Partition version:これは各shardのリーダーが持っているカウンターで、書き込み処理ごとに増加し、レプリカに送られます。
- Cluster Lock:これはrange(※後述されているハッシュ値の範囲のことか?)->パーティションもしくはパーティション->ノードのマッピングを変更するために取得しなければいけないグローバルなロックのことです。
※用語だけだと関係がわかりづらかったので、図を書いてみました。
ドキュメントの集合とパーティションについての考え方
クラスタ、ノード、シャードの考え方。
処理原則
- 任意の処理はクラスタにある任意のノードに実行可能です。
- リカバリできないSPOFはありません。
- クラスタは伸縮自在(elastic)でなければならない
- 書き込みが失われないこと(耐久性)を保証する
- 書き込み順序が保証されなければならない
- 2つのクライアントが2つの「A」というドキュメントを同時に送信してきた場合、すべてのレプリカで一貫してどちらか一方が保存されなければならない。
- クラスタの設定は中央管理されなければならない。また、クラスタのどのノードからもクラスタ設定が更新できます。
- 読み込み(検索)の自動的なフェイルオーバー
- 書き込み(インデクシング)の自動的なフェイルオーバー
- ノードの故障が発生しても自動的にrepcation factorの数は守られます。(故障したら動的にレプリカを再配置?)
Zookeeper
ZooKeeperクラスタは次のために使用されます。
- クラスタ設定の集中管理
- 分散同期に必要な操作のコーディネータ
- クラスタ構成を保存するためのシステム
Partitioning
クラスタは固定されたmax_hash_value=「N」が設定されます。 max_hash_valueは1000のような大きな値が設定されます。
hash = hash_function(doc.getKey()) % N
ハッシュ値の範囲がパーティションに割り当てられ、ZooKeeperに保存されます。 次の例のような形で、パーティションに対して範囲が設定されます。
range : partition
------ ----------
0 - 99 : 1
100-199: 2
200-299: 3
ハッシュはドキュメントにインデックスフィールドとして追加され、変更されない値です。 これは、インデックスを分割するときにも利用します。
ハッシュ関数はプラガブルです。これはドキュメントを受け取り、一貫した正整数ハッシュ値を返します。デフォルトのハッシュ関数として、必須でかつ変更されないフィールド(デフォルトはユニークキーフィールド)からハッシュ値を計算する関数が提供されます。
Using full hash range
max_hash_valueは必ずしも必要ではありません。各shardはいずれにしろハッシュ値の範囲持っているので、完全な32 bitsハッシュを使うこともできます。 設定可能なmax_hash_valueを利用しないで、クライアントからの値をもとにハッシュ値を作ることができます。 例えば、電子メールの検索アプリでは次のようにハッシュ関数を作ることができます。
(hash(user_id)<<24) | (hash(message_id)>>>8)
ユーザIDから8bitのハッシュコードの先頭8ビットを利用することで、任意のユーザのメールがクラスタの同じ256番目(のノード?)にあるのを保証します。検索時はこの情報をもとにクラスタのその部分への問い合わせだけで情報が得られます。
おそらく、私たちは最大値から最小値をカバーする範囲を表現するのにハッシュ空間を輪(固定のハッシュではなく)とみなしたいです。(???円状のハッシュ空間とすることで、クラスタ内のノード数の増減に耐えられるようにするよということかな?)
shard naming
シャードからハッシュ値の範囲へのマッピングを別々に管理するよりも、ハッシュコードによりパーティションを構成するときに実際にはハッシュの範囲をシャード名にします。 (シャード「1-1000」は1から1000の間のハッシュコードを持つドキュメントが含まれるという形)
現時点では(コレクション1つに対してシングルコアの1Solrサーバと仮定して)solrコア名はコレクション名をつけるようになっています。 同一コレクションのためのマルチコアに対してのいい命名規則をつけるという課題が残っています。 (※コレクションに対する説明がここまでないかな?)
Shard Assignment
ノード->パーティションのマッピングはZooKeeperにあるCluster Lockを取得したノードによってのみ変更が可能です。 ノードの追加時に、まず、Cluster Lockを取得し、次にそれがどのパーティションを取得できるかを識別します。
Node to a shard assignment
新しいノードを探しているノードはまずCluster Lockを取得しないといけません。 第一に、リーダーはシャードを決めます。 シャードが持つ、すべての利用可能なノード数で最小の値を持つノードが選び出されます。 もし、同値ならランダムにノードを選びます。
原文はこちらからです。
New SolrCloud Design
(Work in progress)
What is SolrCloud?
SolrCloud is an enhancement to the existing Solr to manage and operate Solr as a search service in a cloud.
Glossary
- Cluster : Cluster is a set of Solr nodes managed as a single unit. The entire cluster must have a single schema and solrconfig
- Node : A JVM instance running Solr
- Partition : A partition is a subset of the entire document collection. A partition is created in such a way that all its documents can be contained in a single index.
- Shard : A Partition needs to be stored in multiple nodes as specified by the replication factor. All these nodes collectively form a shard. A node may be a part of multiple shards
- Leader : Each Shard has one node identified as its leader. All the writes for documents belonging to a partition should be routed through the leader.
- Replication Factor : Minimum number of copies of a document maintained by the cluster
- Transaction Log : An append-only log of write operations maintained by each node
- Partition version : This is a counter maintained with the leader of each shard and incremented on each write operation and sent to the peers
- Cluster Lock : This is a global lock which must be acquired in order to change the range -> partition or the partition -> node mappings.
Guiding Principles
- Any operation can be invoked on any node in the cluster.
- No non-recoverable single point of failures
- Cluster should be elastic
- Writes must never be lost i.e. durability is guaranteed
- Order of writes should be preserved
- If two clients send document “A” to two different replicas at the same time, one should consistently “win” on all replicas.
- Cluster configuration should be managed centrally and can be updated through any node in the cluster. No per node configuration other than local values such as the port, index/logs storage locations should be required
- Automatic failover of reads
- Automatic failover of writes
- Automatically honour the replication factor in the event of a node failure
Zookeeper
A ZooKeeper cluster is used as:
- The central configuration store for the cluster
- A co-ordinator for operations requiring distributed synchronization
- The system-of-record for cluster topology
Partitioning
The cluster is configured with a fixed max_hash_value (which is set to a fairly large value, say 1000) ‘N’. Each document’s hash is calculated as:
hash = hash_function(doc.getKey()) % N
Ranges of hash values are assigned to partitions and stored in Zookeeper. For example we may have a range to partition mapping as follows
range : partition
------ ----------
0 - 99 : 1
100-199: 2
200-299: 3
The hash is added as an indexed field in the doc and it is immutable. This may also be used during an index split
The hash function is pluggable. It can accept a document and return a consistent & positive integer hash value. The system provides a default hash function which uses the content of a configured, required & immutable field (default is unique_key field) to calculate hash values.
Using full hash range
Alternatively, there need not be any max_hash_value - the full 32 bits of the hash can be used since each shard will have a range of hash values anyway. Avoiding a configurable max_hash_value makes things easier on clients wanting related hash values next to each other. For example, in an email search application, one could construct a hashcode as follows:
(hash(user_id)<<24) | (hash(message_id)>>>8)
By deriving the top 8 bits of the hashcode from the user_id, it guarantees that any users emails are in the same 256th portion of the cluster. At search time, this information can be used to only query that portion of the cluster.
We probably also want to view the hash space as a ring (as is done with consistent hashing) in order to express ranges that wrap (cross from the maximum value to the minimum value).
shard naming
When partitioning is by hash code, rather than maintaining a separate mapping from shard to hash range, the shard name could actually be the hash range (i.e. shard “1-1000” would contain docs with a hashcode between 1 and 1000).
The current convention for solr-core naming is that it match the collection name (assuming a single core in a solr server for the collection). We still need a good naming scheme for when there are multiple cores for the same collection.
Shard Assignment
The node -> partition mapping can only be changed by a node which has acquired the Cluster Lock in ZooKeeper. So when a node comes up, it first attempts to acquire the cluster lock, waits for it to be acquired and then identifies the partition to which it can subscribe to.
Node to a shard assignment
The node which is trying to find a new node should acquire the cluster lock first. First of all the leader is identified for the shard. Out of the all the available nodes, the node with the least number of shards is selected. If there is a tie, the node which is a leader to the least number of shard is chosen. If there is a tie, a random node is chosen.
comments powered by Disqus
See Also by Hugo
- New SolrCloud Designの翻訳(その2)(Jugemより移植)
- Elasticsearch unplugged - 2.0におけるネットワークの変更(日本語訳)
- Elasticsearch 1.7.0 および 1.6.1リリース(日本語訳)
- elastic-you-know-for-more-than-search-ja
- elasticsearch-kopfの紹介(概要)